Mycobacterium kansasii infection in a psoriasis patient treated with adalimumab and switch to apremilast: First report and literature review
Accepted: 16 November 2020
HTML: 2
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
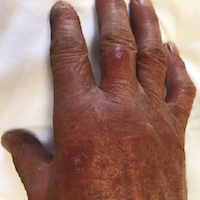
Patient under anti-TNF-alpha treatment have an increased risk of mycobacterial infections, particularly tuberculosis. Only four case reports of Mycobacterium kansasii infection under anti-TNF-α treatment (two with etanercept, two with infliximab) have been reported, but none under adalimumab. A 72-year-old man treated with adalimumab for psoriasis vulgaris and arthropathic psoriasis, complained on nocturnal cough, occasional hemoptysis and the new onset of ill-defined, reddish, asymptomatic persistent plaques-nodules covered by serum crusts on his back, on the dorsum of the right hand and right middle finger. Routine laboratory investigations, HIV and TB screening (QuantiFERON-TB-Gold test) were all within normal limits. A skin biopsy was inconclusive and special staining resulted negative for microorganisms. Only PCR identified M. kansasii. The patient stopped adalimumab and started anti-TB treatment with gradual improvement of the skin lesions. At 26 months follow-up visit no signs or symptoms of relapse of M. kansasii disease occurred.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2021.8797
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2021.8797



