Erythrodermic psoriasis improved by tildrakizumab
Accepted: 5 March 2022
HTML: 16
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
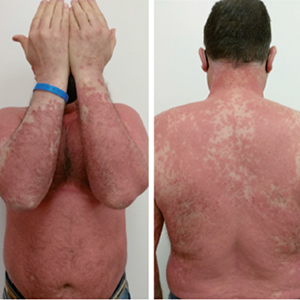
Erythrodermic psoriasis (EP), clinically defined as prominent erythema and scaling affecting almost the entire skin surface, is a severe form and a rare variant of psoriasis. The treatment may require hospital admission with monitoring of vital signs and use of immunosuppressive drugs. Newer biological drugs, including anti-TNF, anti-IL-17, and anti-IL-23 agents, even if not specifically developed for the treatment of erythrodermic psoriasis, have been used successfully in single cases or small case series. Tildrakizumab is an IgG1ҡ monoclonal antibody that selectively binds to the p19 subunit thus inhibiting the interaction of interleukin 23 (IL-23) with its receptor and suppressing the release of IL-23-mediated proinflammatory cytokines. We present a case of EP in an obese man (Body mass index 35.2) who was successfully and safely treated with tildrakizumab.
Rosenbach M, Hsu S, Korman NJ, et al. Treatment of erythrodermic psoriasis: from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010;62:655–62.
Boyd AS, Menter A. Erythrodermic psoriasis. Precipitating factors, course, and prognosis in 50 patients. J Am Acad Dermatol 1989;21:985–91. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0190-9622(89)70287-5
Lo Y, Tsai TF. Updates on the Treatment of Erythrodermic Psoriasis. Psoriasis (Auckl). 2021;11:59-73. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/PTT.S288345
Singh RK, Lee KM, Ucmak D, et al. Erythrodermic psoriasis: pathophysiol-ogy and current treatment perspectives. Psoriasis (Auckl) 2016;6:93-104. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/PTT.S101232
Zhang P, Chen H, Duan Y, et al. Analysis of Th1/Th2 response pattern for erythrodermic psoriasis. J Huazhong Univ Sci Tech Med Sci 2014;34:596–601. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11596-014-1322-0
Li LF, Sujan SA, Yang H, Wang WH. Serum immunoglobulins in psoriatic erythroderma. Clin Exp Dermatol 2005;30:125–7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01717.x
Deeva I, Mariani S, De Luca C, et al. Wide-spectrum profile of inflammatory mediators in the plasma and scales of patients with psoriatic disease. Cytokine 2010;49:163–70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cyto.2009.09.014
Groves RW, Kapahi P, Barker JN, et al. Detection of circulating adhesion molecules in erythrodermic skin dis-ease. J Am Acad Dermatol 1995;32:32–6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/0190-9622(95)90180-9
Moy AP, Murali M, Kroshinsky D, et al. Immunologic Overlap of Helper T-Cell Subtypes 17 and 22 in Erythrodermic Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis. JAMA Dermatol 2015;151:753–60. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2015.2
Shao S, Wang G, Maverakis E, Gudjonsson JE. Targeted Treatment for Erythrodermic Psoriasis: Rationale and Recent Advances. Drugs 2020;80:525-34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40265-020-01283-2
European Medicines Agency. IlumetriTM (tildrakizumab): EU sum-mary of product characteristics. 2018.
Puig L. The role of IL 23 in the treatment of psoriasis. Expert Rev Clin Immunol 2017;13:525-34. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/1744666X.2017.1292137
McGeachy MJ, Chen Y, Tato CM, et al. The interleukin 23 receptor is essential for the terminal differentiation of inter-leukin 17-producing effector T helper cells in vivo.
Lee E, Trepicchio WL, Oestreicher JL, et al. Increased expression of inter-leukin 23 p19 and p40 in lesional skin of patients with psoriasis vulgaris. J Exp Med 2004;199:125–30. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20030451
Fitch E, Harper E, Skorcheva I, et al. Pathophysiology of psoriasis: recent advances on IL-23 and Th17 cytokines. Curr Rheumatol Rep 2007 9:461-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-007-0075-1
Rosenbach M, Hsu S, Korman NJ, et al. Treatment of erythrodermic psoria-sis: from the medical board of the National Psoriasis Foundation. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010;62:655-62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2009.05.048
Carrasquillo OY, Pabón-Cartagena G, Falto-Aizpurua LA, et al. Treatment of erythrodermic psoriasis with biologics: a systematic review. J Am Acad Dermatol 2020;83:151–8. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2020.03.073
Reynolds KA, Pithadia DJ, Lee EB, et al. A systematic review of treatment strategies for erythrodermic psoriasis. J Dermatolog Treat 2021;32:49-55. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1080/09546634.2019.1689228
Megna M, Potestio L, Fabbrocini G, Cinelli E Tildrakizumab: A new thera-peutic option for erythrodermic psoria-sis? Dermatol Ther 2021;34:e15030. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/dth.15030
Burlando M, Castelli R, Cozzani E. Parodi A. Treatment of moderate-to-severe- plaque psoriasis with tildrak-izumab in the real-life setting. Drugs Context 2021;10:2021. DOI: https://doi.org/10.7573/dic.2021-2-6
Copyright (c) 2022 the Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2022.9448
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2022.9448



