Keratolysis exfoliativa-like eruption induced by ranolazine
Accepted: 12 July 2021
HTML: 117
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
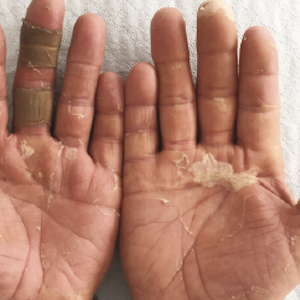
Dermatoses affecting palms may represent a dermatologic challenge from both the diagnostic, and therapeutic point of view. Patients with supposedly occupational dermatitis can spend months or even years in a frustrating attempt to avoid contact with possible irritants or allergens. To underline the importance of a thorough unbiased analysis of the patient’s history and clinical features, we present the iconic case of a bricklayer affected by a chronic, disabling desquamation of palms which in the end was classified as keratolysis exfoliativa (KE) attributed to ranolazine-intake, an antianginal drug. To the best of our knowledge, this specific adverse effect of druginduced KE of palms has never been reported before in association with ranolazine.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2022.9264
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2022.9264



