Anti-interleukin-17 and anti-interleukin-23 biologic drugs for genital psoriasis: a single-center retrospective comparative study
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
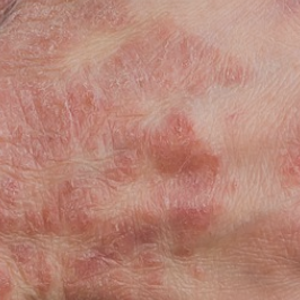
Genital psoriasis affects 3-33% of patients with psoriasis during the course of the disease, usually leading to a severe reduction in the patient’s quality of life. This study aims to retrospectively assess the effectiveness of interleukin (IL)-23 and IL-17 inhibitors in a real-life population affected by moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis with genital involvement coming from our dermatology department. A total of 86 patients with a diagnosis of moderate-tosevere plaque psoriasis with severe genital involvement were enrolled. Patient characteristics, psoriasis area and severity index (PASI), and static physician global assessment of genitalia (sPGAG) at each visit were recorded. During the treatment, the mean PASI decreased from 12.8 to 0.63 at week 52; a PGA of 0/1 was reached by 97.40% at week 52 and by 100% of patients (37/37) at week 104. No significant differences between IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors were observed; indeed, the bio-naïve group of patients demonstrated a superior response compared to the group of bioexperienced patients.Our findings confirmed that IL-23 and IL-17 inhibitors are safe and effective therapeutic options for the treatment of genital psoriasis.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2023.9692
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2023.9692