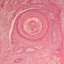
Seborrheic keratosis evolution into squamous cell carcinoma: A truly modified sun-related tumor? A case report and review of the literature
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
The incidence of seborrheic keratosis (SK) generally increases with age and are mostly localized on the trunk, face and neck, especially on sun-exposed areas. The association between SK and skin malignancies appears to be accidental, but in situ transformation occurs more frequently in sun-exposed areas. Histopathological examination of all SK cases should be considered, especially when SK lesions exhibit atypical clinical manifestations, such as ulceration and cresting, as they may herald malignant transformation. In addition, other features associated with malignant transformation include excoriations or hemorrhages identified on the lesion, modification and evolution of the macroscopic characteristics, and the presence of local erythema or pruritus. Immunocompromised patients exhibit an increased risk of malignant transformation, even when radiation is involved.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2019.7999
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2019.7999