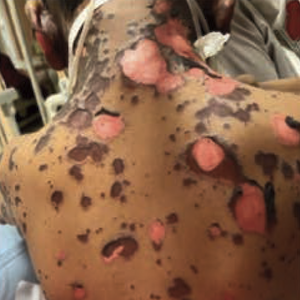
Combination of cyclosporine A and methylprednisolone to treat pediatric Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis overlap syndrome
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Authors
- Shinta Trilaksmi Dewi Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. https://orcid.org/0000-0001-8972-4379
- Laily Noor Qomariah Wates Government District Hospital, Kulon Progo, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
- Widya Khairunisa Sarkowi Faculty of Medicine, IPB University, Bogor, West Java, Indonesia. https://orcid.org/0000-0002-3974-5371
- Monika Puspitasari Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
- Miya Khalidah Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. https://orcid.org/0000-0001-5730-9306
- Marcella Anggatama Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
- Dwinanda Almira Rizkiani Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia. https://orcid.org/0000-0003-3172-1962
- Kristiana Etnawati Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
- Sri Awalia Febriana Department of Dermatology and Venereology, Faculty of Medicine, Public Health and Nursing, Gadjah Mada University, Yogyakarta, Indonesia.
The treatment of epidermal necrolysis in pediatric patients remains a major challenge. Cyclosporine A has emerged as a promising therapy for epidermal necrolysis in adults; however, its efficacy in children is unclear. We present the case of a boy with Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis overlap syndrome who was initially resistant to methylprednisolone monotherapy but improved after receiving the combination of cyclosporine A and methylprednisolone. Published reports on the use of cyclosporine A for pediatric epidermal necrolysis are also briefly reviewed.
Frantz R, Huang S, Are A, Motaparthi K. Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a review of diagnosis and management. Medicina (Kaunas) 2021;57:1-15. DOI: https://doi.org/10.3390/medicina57090895
Hsu DY, Brieva J, Silverberg NB, et al. Pediatric Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in the United States. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017;76:811-7.e4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2016.12.024
Abtahi-Naeini B, Dehghan MS, Paknazar F, et al. Clinical and epidemiological features of patients with drug-induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in Iran: different points of children from adults. Int J Pediatr 2022;2022:1-10. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/8163588
Ramien M, Goldman JL. Pediatric SJS-TEN: Where are we now? F1000Res 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-982. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.20419.1
Liotti L, Caimmi S, Bottau P, et al. Clinical features, outcomes and treatment in children with drug induced Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Acta Biomed 2019; 90:52-60.
Antoon JW, Goldman JL, Lee B, Schwartz A. Incidence, outcomes, and resource use in children with Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Pediatr Dermatol 2018;35:182-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/pde.13383
Hasegawa A, Abe R. Recent advances in managing and understanding Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. F1000Res 2020;9:F1000 Faculty Rev-612. DOI: https://doi.org/10.12688/f1000research.24748.1
Zimmermann S, Sekula P, Venhoff M, et al. Systemic immunomodulating therapies for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. JAMA Dermatol 2017;153:514-22. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1001/jamadermatol.2016.5668
Renfro L, Grant‐Kels JM, Daman LA. Drug‐induced toxic epidermal necrolysis treated with cyclosporin. Int J Dermatol 1989;28:441-4. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4362.1989.tb02502.x
Auyeung J, Lee M. Successful treatment of Stevens–Johnson syndrome with cyclosporine and corticosteroid. Can J Hosp Pharm 2018;71:272. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4212/cjhp.v71i4.2829
Yu R, Chen S, Pan Y, et al. Combined use of cyclosporine in the treatment of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Dermatol 2022;49:629-36. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/1346-8138.16369
Coulombe J, Belzile E, Duhamel A, et al. Pediatric SJS/TEN subdued by a combination of dexamethasone, cyclosporine, and etanercept. J Cutan Med Surg 2019;23:547-50. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1177/1203475419861078
St John J, Ratushny V, Liu KJ, et al. Successful use of cyclosporin A for Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis in three children. Pediatr Dermatol 2017;34:540-6. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/pde.13236
Alajmi A, Jfri A, Gomolin A, Jafarian F. A pediatric case of Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis with rapid response to intravenous cyclosporine. JAAD Case Rep 2020;6:555-7. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.04.003
Szepietowski J, Wa̧sik F, Szybejko-Machaj G, Maj J. Toxic epidermal necrolysis successfully treated with cyclosporin: report of three cases. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 1997;9:169-72. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/S0926-9959(97)00047-0
Aihara Y, Ito R, Ito S, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a child successfully treated with cyclosporin A and methylprednisolone. Pediatr Int 2007;49:659-62. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1442-200X.2007.02439.x
Sato S, Kanbe T, Tamaki Z, et al. Clinical features of Stevens-Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis. Pediatr Int 2018;60:697-702. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1111/ped.13613
Zielińska M, Matusiak Ł, Golębiowski W, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in an 8-year-old girl successfully treated with cyclosporin A, intravenous immunoglobulin and plasma exchange. Postepy Dermatol Alergol 2018;35:217-21. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5114/ada.2018.75247
Quintana-Castanedo L, Nieto-Rodríguez D, Rodríguez-Álvarez D, et al. Toxic epidermal necrolysis in a boy: successful treatment with cyclosporine A. Actas Dermosifiliográficas (Engl Ed) 2021;112:468-70. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.adengl.2021.02.013
Cruz-Topete D, Cidlowski JA. One hormone, two actions: anti- and pro-inflammatory effects of glucocorticoids. Neuroimmunomodulation 2015;22:20-32. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1159/000362724
Amor KT, Ryan C, Menter A. The use of cyclosporine in dermatology: part I. J Am Acad Dermatol 2010;63: 925-46. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2010.02.063
Ng QX, De Deyn M, Venkatanarayanan N, et al. A meta-analysis of cyclosporine treatment for Stevens-Johnson syndrome/toxic epidermal necrolysis. J Inflamm Res 2018;11:135-42. DOI: https://doi.org/10.2147/JIR.S160964
Kumar P, Kanti Das N. Cyclosporine in toxic epidermal necrolysis: a brief review of the emerging therapeutic modality. Dermatol Online J 2016;22:13030. DOI: https://doi.org/10.5070/D32210032890
Singh GK, Chatterjee M, Verma R. Cyclosporine in Stevens Johnson syndrome and toxic epidermal necrolysis and retrospective comparison with systemic corticosteroid. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2013;79:686-92. DOI: https://doi.org/10.4103/0378-6323.116738
Weber LT, Armstrong VW, Shipkova M, et al. Cyclosporin A absorption profiles in pediatric renal transplant recipients predict the risk of acute rejection. Ther Drug Monit 2004;26:415-24. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1097/00007691-200408000-00012
Copyright (c) 2023 the Author(s)

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.
PAGEPress has chosen to apply the Creative Commons Attribution NonCommercial 4.0 International License (CC BY-NC 4.0) to all manuscripts to be published.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2023.9656
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2023.9656