Rituximab for linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
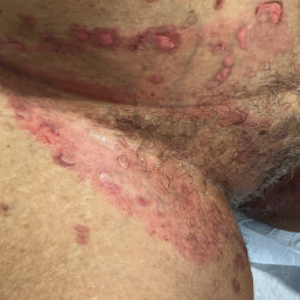
Linear immunoglobulin A bullous dermatosis (LABD) is an idiopathic or drug-induced vesiculobullous disease typically managed with dapsone or colchicine. We report a case of LABD successfully treated with rituximab in a patient who was intolerant to first-line therapies and recalcitrant to typical immunosuppressants. The patient was initially started on prednisone and mycophenolate mofetil which resulted in minimal response and disease progression. Improvement was seen after two infusions of rituximab 1000 mg at 2 weeks apart with planned maintenance therapy.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2023.9574
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2023.9574