Increased serum interleukin-17A levels correlate with disease severity and poor prognostic factors in patients with alopecia areata
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
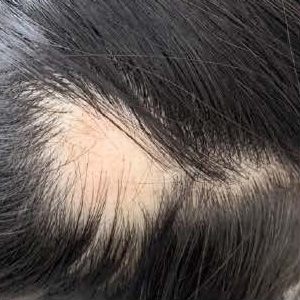
Alopecia areata (AA) is a tissue-specific autoimmune disease characterized by non-scarring and rapid onset of hair loss. Interleukin (IL)-17A is mainly produced by T helper 17 (Th17) cells and may play a crucial role in the pathogenesis of various autoimmune diseases including AA. We conducted this research to measure serum level of IL-17A in patients with AA and investigated its relationship with the clinical manifestations in patients with AA. We assessed 36 patients with AA and 20 healthy control subjects. Demographic information and clinical characteristics were determined by physical examination and via the review of medical history. Serum IL-17A was measured by using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Serum IL-17A concentration was significantly higher in patients with AA than in the control group (P=0.004). The AA patients with severe presentation, personal atopy, nail abnormalities, or active phase had significantly higher serum IL-17A levels compared to others without these signs. Increased serum IL-17A levels in patients with AA correlate with severity and indicate an active disease state. These findings suggest that IL-17A may play an important role in determining the pathogenesis of AA and may serve as a valuable clinical biomarker of this disease.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2021.9398
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2021.9398