Bullous pemphigoid and radiotherapy: case report and literature review update
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
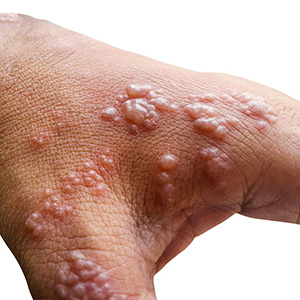
Bullous pemphigoid (BP) is a common autoimmune bullous disease generally occurring in elderly patients. Itchy and tense blisters on normal skin or erythematous and edematous lesions on the trunk and extremities usually characterize BP. Trigger factors are still unclear while several case reports suggest a potential role of radiotherapy (RT) as BP trigger for disease onset or recrudescence. A review was performed to provide an update of literature. A case report of a patient affected by BP undergoing two radiotherapy courses for a primary breast cancer was also reported. A comprehensive review of the published literature was conducted according to Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. The review included studies describing BP and its relationships with RT treatments. A total of 13 articles were reviewed. Studies characteristics analysis resulted in eleven case reports, one case series and one large-scale case– control study. Literature update confirms the existence of a reasonable connection between RT and BP. Case report showed that a multidisciplinary management seems to assure the feasibility of RT in patients affected by BP, not depriving them of standard therapeutic opportunities.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2022.9170
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2022.9170