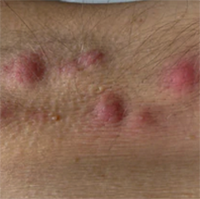
Secondary prevention of hidradenitis suppurativa
 Smart Citations
Smart CitationsSee how this article has been cited at scite.ai
scite shows how a scientific paper has been cited by providing the context of the citation, a classification describing whether it supports, mentions, or contrasts the cited claim, and a label indicating in which section the citation was made.
Hidradenitis suppurativa (HS) is a multifactorial disease with many facets of uncertain importance for optimal treatment and prevention. In order to explore options for secondary prevention in HS, we randomly and retrospectively selected 40 patients with HS that were analyzed on the basis of supposed trigger factors and proposed prevention measures. 67% of our HS patients were current smokers. They had started smoking on average 8 years prior to abscess formation. 35% complained of digestive problems and had tried different sorts of diet. We identified 2 cases of gluten-sensitive enteropathy, in which HS improved after introduction of gluten-free diet. In 7 further patients, introduction of low dairy/low carbohydrate diet considerably improved HS. 77.5% had never used any skin care in the intertriginous areas. Implementing secondary prevention by reducing irritation, avoiding shaving, improving skin care, performing laser epilation or applying fusidic acid/betamethasone cream led to an improvement in 62.5% of patients. We suggest a structured approach in daily practice in order to identify individual trigger factors. The crucial point for secondary prevention is the improvement of patient education.





 https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2019.8243
https://doi.org/10.4081/dr.2019.8243